The American Gem Society (AGS) is one of the most respected diamond grading organizations in the industry, known for its stringent grading standards and cutting-edge technology. Founded in 1934, the AGS aims to set high ethical and professional criteria for the jewelry trade. While the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) is often considered the gold standard for diamond certification, AGS is held in similar regard, particularly for its expertise in cut grading. The AGS utilizes a numerical scale of 0 to 10 for its diamond grades, with 0 being the highest quality.
When it comes to reliability, the AGS is highly trustworthy, and many experts recommend buying a diamond with an AGS certification. This is especially true if you’re considering a diamond where the quality of the cut is a significant factor, as AGS’s cut grading is considered by many to be the best in the industry. However, it’s crucial to compare AGS-graded diamonds with those graded by other reputable labs like GIA to ensure you’re getting the best value. Both AGS and GIA offer comprehensive certification that includes assessments of a diamond’s 4Cs—cut, color, clarity, and carat weight—making either a reliable choice for diamond grading.
Bottom Line Recommendation:
The AGS has established itself as a top-tier diamond grading organization. As one of the most reliable and reputable lab grading entities, we recommend buyers seek an AGS certified diamond (or a GIA certified diamond). When choosing an AGS diamond, be sure to buy from a high-quality diamond vendor, like Blue Nile or James Allen.
History of AGS
In 1934, a small group of jewelers who wanted to protect buyers from false advertising and fraud in the diamond industry established the American Gem Society (AGS). They were the first organization to release a diamond cut grading system when they did so in 1966.
Today, the AGS provides retailers, jewelers and individuals with gemological knowledge, research, consumer protection and standard grading of diamonds. With clear and consistent grading, the AGS is one of the most trusted lab grading entities in the world.
Why you should trust us
AGS Diamond Grading Report
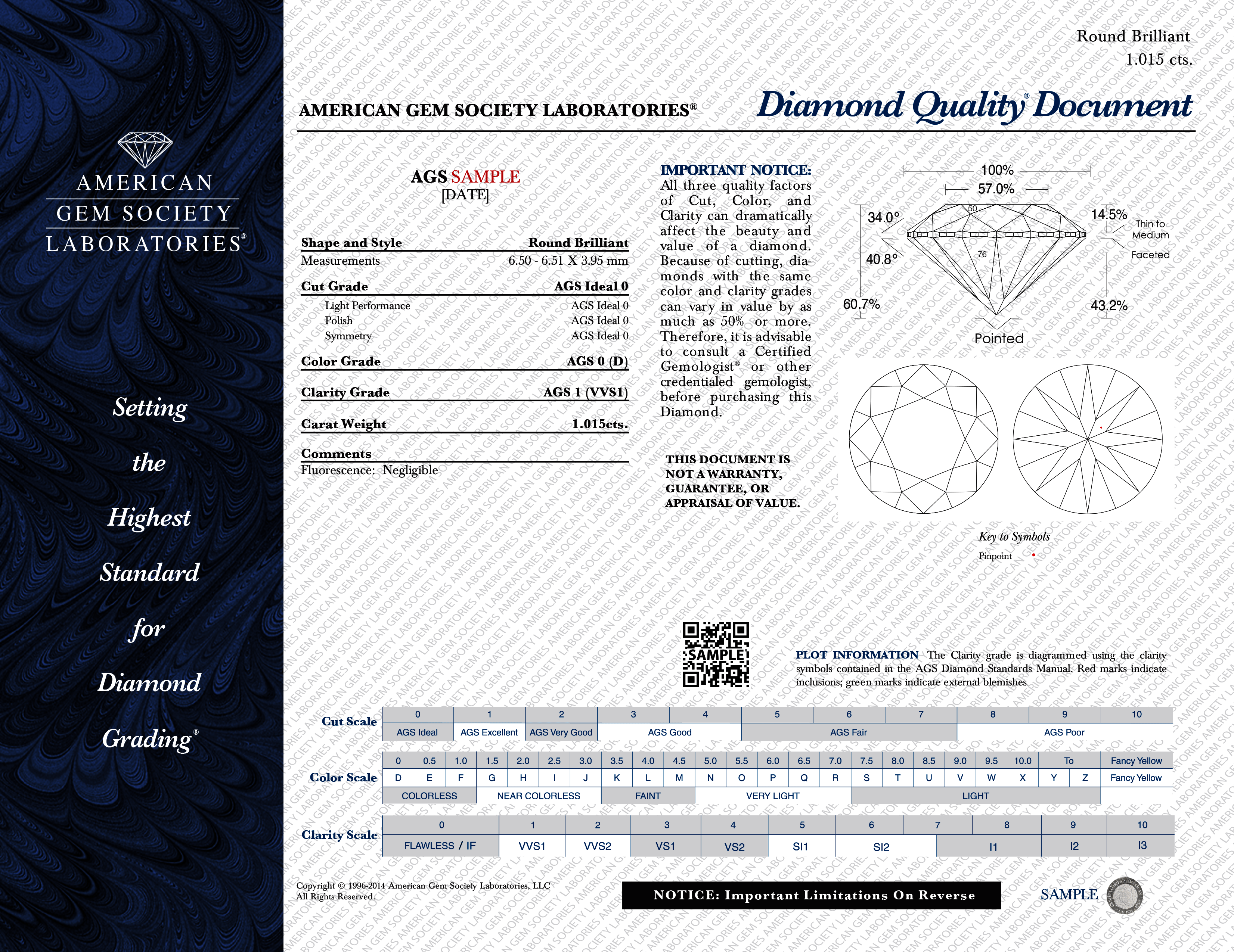
The AGS evaluates each diamond based on its qualities and components. It issues a grading report that includes details on everything from the cut quality to the carat weight. When reviewing an AGS diamond grading report, look at each aspect to verify what you’re buying.
Diamond Quality Report
The AGS diamond quality report gives you grading and description of the diamond you’re buying. It’s a complete analysis offered for round brilliant, oval, emerald, princess, and cushion cut diamonds.
As you can see in the report below, the AGS diamond grading for the cut, color, clarity, and carat are all listed. There are further details under Cut such as light performance, symmetry and polish. You can also see important measurements of the diamond’s table, pavilion, and other components. There’s also a plot showing any inclusions on the diamond.
By looking at an AGS report, you can evaluate the diamond more easily to see if it’s the stone you’d like to buy.
You can even do an AGS cert lookup to verify that the AGS diamond report you received matches the AGS database. This helps ensure the authenticity of the report the jeweler gave you.
Gold Diamond Quality Report
AGS gold diamond quality reports are issued specifically for round brilliant diamonds. It includes a proportion-based report, detailing aspects like table size and girdle thickness. AGS has 3D technology that helps evaluate Cut quality in more detail. The report still gives a full analysis and grading of other aspects such as carat weight, color, and clarity.
A sample of a gold diamond quality report is below.
Other AGS Diamond Reports
Besides the diamond quality report and gold diamond quality report, AGS issues a range of certificates depending on the diamond and what the jeweler requested. These reports include the Platinum Diamond Quality Document (sample image below), the Diamond Quality Analysis, and the Diamond Consultation.
As a non-profit independent grading entity, the AGS has no stake in the sale of a diamond. Therefore, AGS is not incentivized to issue grading that helps the seller.
AGS vs. GIA: Grading Results and Scale
A diamond’s authenticity and quality is measured by the 4Cs and the diamond grading organization. Among all the diamond certificates, the AGS and GIA are the most reputable and reliable in the industry. A 4 C’s of diamonds (cut, color, clarity and carat) represent the four main components oftheirs structure and beauty. AGS grades each C on a scale—helping to determine the value of a diamond and its level of quality.
The only difference between AGS and GIA is the parameters for measuring cut quality. With AGS, the cut grading scale is from 0-10 (along with descriptive wording), 0 means Ideal and 8-10 means Poor. The GIA scale includes Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair and Poor. A diamond graded for its cut by either the GIA or AGS is valid and reliable. They both indicate if a diamond has a quality cut. For example, we recommend only considering diamonds graded as 0 or 1 on the AGS scale and or Excellent on the GIA scale.
Besides cut, the remaining qualities graded by AGS or GIA overlap with each other, based on how they assess that diamond component. The scales match up, but the grading number and names may be slightly different. We outline the AGS vs. GIA grading scales below.
Cut
Diamond cut indicates the quality of a diamond’s angles, proportions, symmetrical facets, brilliance, fire, scintillation and finishing details.
Cut is graded differently by the AGS and GIA. The AGS assigns a number along with a descriptive word grading.
The AGS cut scale is as follows from grade 0 to 9, 0 being ideal and 10 meaning poor:

The Ideal and Excellent grades, depending on shape, demonstrate proportions and angles cut for maximum fire and brilliance.
It’s important to know that a top designation, like Excellent, doesn’t always indicate an outstanding diamond. Almost 55% of diamonds sold online are graded as Excellent cuts. Some are mediocre, while others are stunning like this 1.50 carat round brilliant from James Allen.
Because Cut is critical to a diamond’s beauty, it’s necessary to review Cut quality and ask for an expert’s opinion.
Color
Diamond color grading determines how white or colorless a diamond is. AGS grades diamonds on the following color scale, from 0 to 10 (with 0 being the most colorless and 10 denoting noticeable yellow or brown tint).
The chart below shows how the AGS and GIA color grades overlap with each other. If you are comparing two diamonds, one certified by GIA and one by AGS, you’ll be able to compare their colors using this chart.

In almost all cases, the naked eye is unable to distinguish two adjacently color graded diamonds, although the price difference may be significant. The color grade given by AGS helps identify the quality of the diamond’s Color, yet it’s still important to determine if the diamond appears colorless to your own eye without magnification.
Note: Fancy Diamonds, like a purple or blue diamond, are valued gemstones.
Their color grades are different than those of traditional “white” diamonds.
Clarity
Similar to cut and color, AGS grades clarity on a 10-point scale. Diamond clarity refers to how clean a diamond is from inclusions and blemishes. A clarity grade by the GIA or AGS indicates how many imperfections a diamond has.

For clarity, we recommend looking for a diamond that is eye clean. If you’re unsure how to evaluate a diamond for clarity or any other characteristic, contact one of our experts.
Carat
The weight of a diamond, not its size, is what carat refers to. For perspective, a 1 carat diamond equals 200 milligrams or 0.2 grams—meaning it weighs about the same as a quarter of a raisin. Two 1 carat diamonds can be quite different in size, depending on diamond shape and how the gemstone is cut.
The overall beauty of a diamond should carry more importance than carat weight when deciding which diamond to purchase.
For more detailed information, see our full guide on diamond carat weight.
Proportions
In addition to the 4 C’s, an AGS report provides information about the width, depth and table size of a diamond.
Diamond Table Percentage
To calculate the diamond table %, the width of the table (top surface area) is divided by its width (diameter). If the table facet is 3.5 mm wide, and the diamond is 5 mm wide, the table % is 70%.
An ideal table % depends on the diamond’s shape. To determine if a diamond has a high-quality table %, contact us and we’ll be happy to assist.
Diamond Width
A diamond’s width is measured as the length from one end of its girdle (the diameter at its widest point) to the other end of the girdle. Width is important when it comes to calculating a diamond’s length to width ratio, which determines how proportionate the stone is.
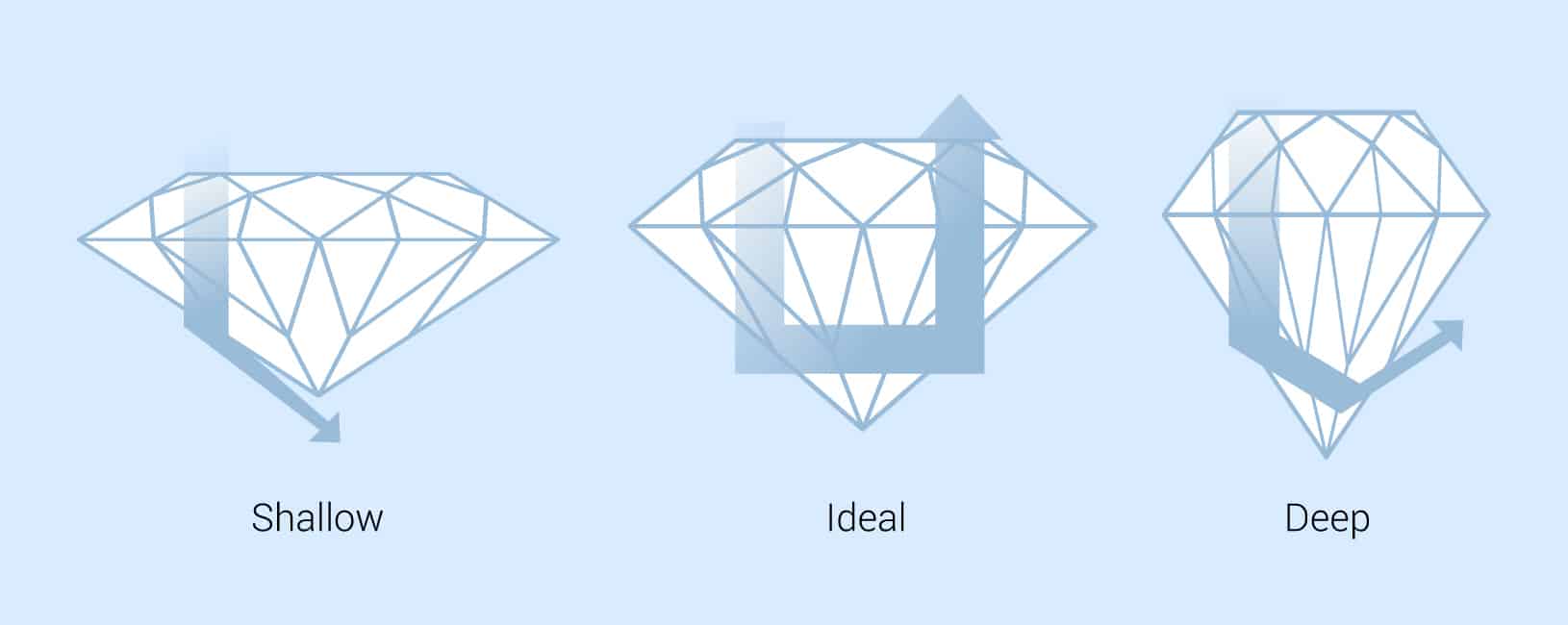
Depth Percentage
The height of the diamond from the culet to the top of the table is considered the depth %. The depth % is calculated by dividing the depth by the width. This measurement is reported in millimeters and percentage. For instance, a diamond of 4mm in depth and 4.5 mm in width would have a depth percentage of 88.8%.
A lower depth % of two equal carat diamonds usually appears larger due to increased width. A depth % that is too low, though, can create a dark appearance as it will not reflect light very well.
Engagement Ring Inspiration (Click a Ring for More Information)
Additional Grading Information
In addition to the 4 C’s and proportions, an AGS report includes further details, like finish, polish, symmetry and diamond fluorescence.
These aspects impact a diamond’s beauty, but they are not the most important components to consider when making a decision.
How AGS Certification Impacts Cost
The fact that a diamond has or doesn’t have an AGS certification does not make the gemstone more expensive. The AGS is an independent grading entity and does not have a stake in the sale of a diamond. Diamonds certified by the AGS sell at similar prices to their GIA equivalents.
Upgrade Shopping
The one issue to look out for is “upgrade shopping”. No lab is 100% accurate as color and clarity are not objective grades (like weight and dimensions are). If there is a diamond that is somewhere in between grades, a manufacturer or retailer may send the diamond to multiple laboratories looking for the better grade. For example, say a diamond is a weak I color or strong J color, and they received a J color from GIA. The wholesaler/retailer may try sending it to AGS for the I color (they can then sell it for much more money). Its far more likely that the grades will be the same, but its possible they will get the upgrade (which more than makes up for the cost of sending it to AGS for certification).
It is very common for companies to use AGS for branded super ideal diamonds (like True Hearts, or Hearts on Fire). But AGS is not as commonly used for non-round diamonds. So if a retailer has 50 cushion cut diamonds, 49 of which are GIA certified and one AGS diamond, that diamond is likely to have received an upgrade.
This is not a knock on AGS, merely an observation of how some wholesalers and retailers may try to take advantage of the end consumer.
Advantages of AGS Certification
- Highly respected certification
- Offers consistent and reliable grading
- Ensures you’re receiving the diamond quality that the certificate states
- Provides six security measures to help ensure authenticity
Disadvantages of AGS Certification
- Be wary of upgrade shopping
Unique Reports and Additional Services
In addition to evaluating diamonds, the AGS provides:
We strongly recommend looking for a diamond that is AGS or GIA Certified. We also encourage purchasing a diamond only from a reputable vendor like Blue Nile or James Allen.
For assistance in reading a report or comparing diamonds, feel welcome to contact our experts.
If you would like to know more about diamond certificates, read our guide on diamond certification.
Here are more specific certificate topics to browse:
- What diamond certification is the best?
- What is the meaning of GIA diamond certification?
- Is IGI diamond certification good / how does it compare vs. GIA?
- How does EGL certification compare vs. GIA?
- How does HRD certification compare vs. GIA?
- Is GSI diamond certification good / how does it compare vs. GIA?
- Does GIA or IGI certify lab-grown diamonds?

- Unsurpassed brilliance
- Offer custom cut diamonds
- Impressive collection of designer engagement rings
- Excellent personalized customer service
- Fifth generation diamond cutter

Still afraid of getting ripped off?
Before you buy a diamond, get personal buying advice from industry veterans. We'll help you get the best diamond for the money.
Ask your diamond purchase question here
DISCLAIMER: We don't use your email for marketing. Period.
You Might Like
Diamond Prices: A Complete Guide
A diamonds’ price is determined primarily by the 4 Cs of the diamond. On the wholesale level, diamond prices are first based on a diamond shape and
The Best Places to Buy Engagement Rings
When purchasing a diamond engagement ring, it’s important to find the right retailer to purchase it from. Some retailers excel at niche products li
1 Carat Diamond Price & Buying Guide
A wide range of 1 carat diamonds exist both in online markets and local diamond jewelry stores. Not only are there significant differences in beauty